Investors are always mindful of opportunities and risk in structuring their investment portfolios. Over the last decade, many have wondered about two questions:
- Do government fiscal policies (i.e., changes in spending and tax regimes) impact investment outcomes over the long haul?
- If so, can one structure a portfolio to take advantage of fiscal policies?
The Tax Side of Fiscal Policies
Let’s start with the tax side of this issue. According to a recent paper from the Brookings Institution, a tax cut could “pay for itself” if it spurred substantial economic growth. The “payment” would derive from higher overall tax revenues resulting from the combination of higher wages and hours worked. In short, the Brookings paper posits that lower corporate taxes could, in theory, result in greater corporate profits and investment returns. In theory. But what does the evidence show?
Over the last decade, corporate tax rates have indeed fallen, as the left-hand chart below indicates. Importantly, the impact of tax policy changes has varied across industries due to specific provisions within the tax code. Both capital gains and dividend tax rates have declined as well, part of a longer-term trend in the postwar period. Curiously, the lower right panel conveys an interesting phenomenon: S&P 500 returns were higher after capital gains tax increases!
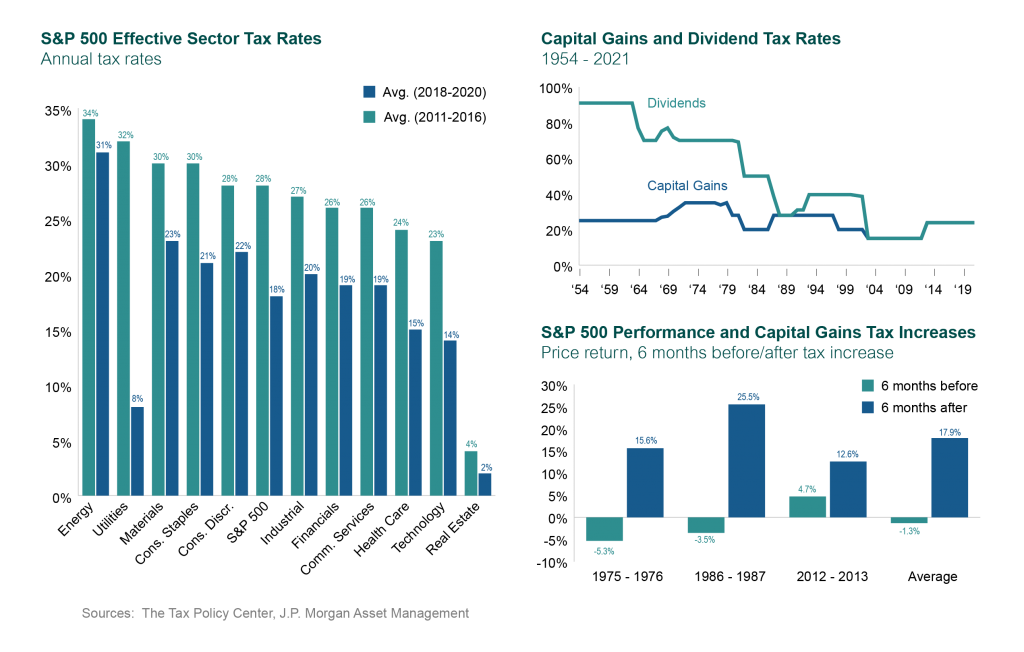
With this backdrop, let’s explore what some recent research has found, specifically analyzing the most recent major changes to federal tax law. A paper in July 2020 from the Cleveland Fed analyzed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act introduced at the end of 2017. The act reduced income tax rates for C corporations (companies that are taxed separately from their owners) from 35 percent to 21 percent.
The Cleveland Fed paper found that some provisions of the act had a positive effect on business investment (e.g., first-year bonus depreciation; the provision on corporate earnings held overseas) while other elements had a negative effect on corporate profitability (e.g., the switch from expensing to amortizing R&D expenses; new limits on interest deductibility).
Overall, the author concluded that the act’s initial impact on business investment was small.
In another recent paper, the Brookings Economic Studies Program found that investment growth rose after the tax cut act was enacted, but this was driven by trends in aggregate demand, oil prices, and intellectual capital that were unrelated to the tax cuts’ supply-side incentives. Growth in business formation, employment, and median wages slowed after the act was enacted.
International profit shifting fell only slightly, and the boost in repatriated profits primarily led to increased share repurchases rather than new investment. At the same time, U.S. multinational corporations increased their foreign capital expenditures after the act was enacted. But—as shown in a paper from the UNC Tax Center at the University of North Carolina Kenan-Flagler Business School and an article published by the Urban Brookings Tax Policy Center—foreign investment in the United States did not rise.
According to the authors of the Brookings research, the tax cut act reduced tax revenues received by the government from individuals and corporations.
Another Aspect of Fiscal Policies
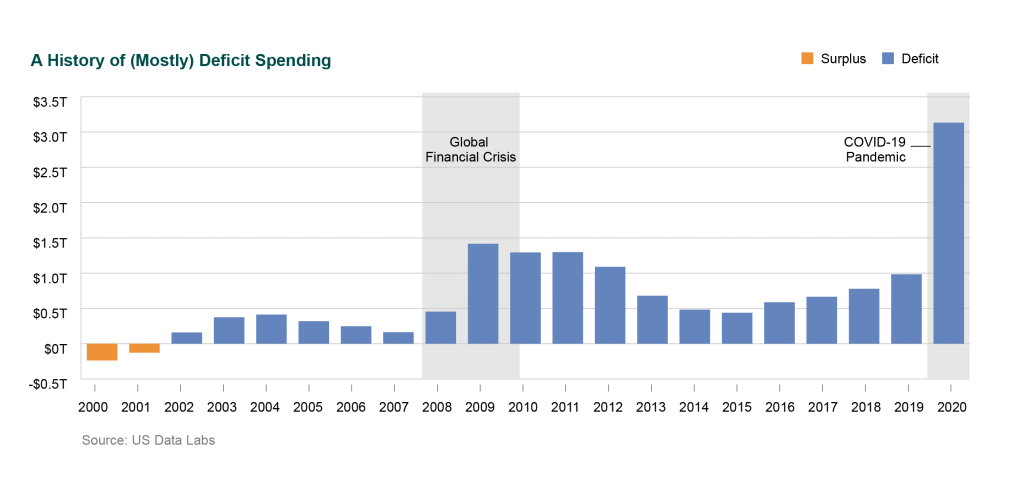
Let’s now take a look at the other major element of fiscal policies, government spending, and how investment returns have fared over the last two decades. Beginning in 2016, increases in spending on Social Security, health care, and interest on the federal debt have outpaced the growth of federal revenue, and of course government spending shot up significantly during 2020 as a result of the pandemic.
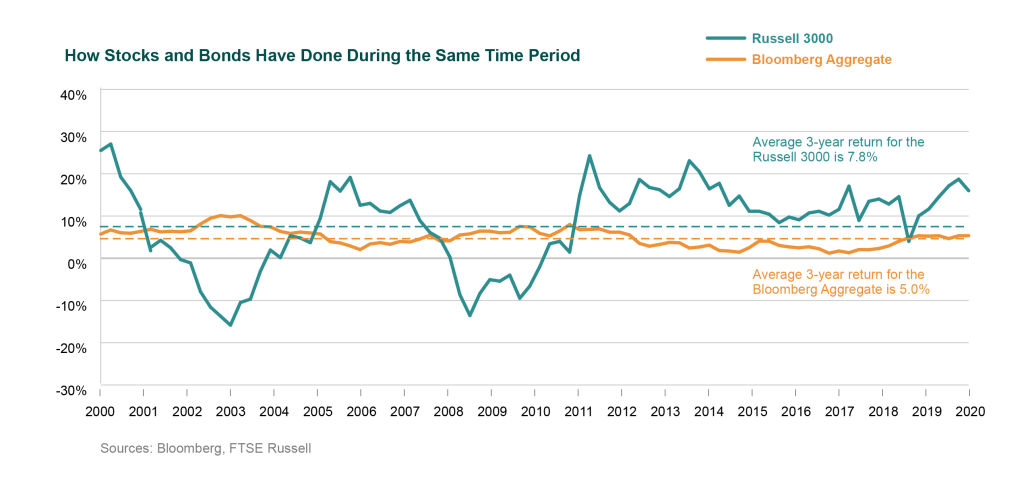
The U.S. stock market declined during the Dot-Com Bubble (2000-02) and the Global Financial Crisis (2008-09), but fixed income returns have produced consistently positive rolling three-year returns throughout the last 21 years in spite of the federal deficit and the government’s resulting need to fund that deficit in the capital markets.
In conclusion, do fiscal policies influence investment returns? Yes, but . . .
There does not appear to be a clear causal link between governmental policies and investment returns. One challenge is that the research yields no clear connection because of other, potentially countervailing forces. Among the non-governmental policy factors that influence investment risk and opportunity in the capital markets:
- Interest rates
- Investor sentiment
- Political environment
- Labor supply and employment levels
- Natural disasters
- Current events
- Currency exchange rates and trade conditions
- Inflation
- Technological innovation
- Demographic trends
Is there a direct connection between fiscal policies to investment outcomes? Mmmm, sort of. The truth of the matter is that multiple factors influence the investing environment, and no single factor in isolation controls investment outcomes.