Each year, Callan surveys institutional investors to better understand their views on environmental, social, and governance principles, and the trends driving ESG adoption. In our recently published 2020 ESG Survey, we found that 42% of respondents incorporated ESG into their investment decision-making process, in line with the previous year’s level. But that figure has nearly doubled from the 22% of investors that incorporated ESG in 2013.
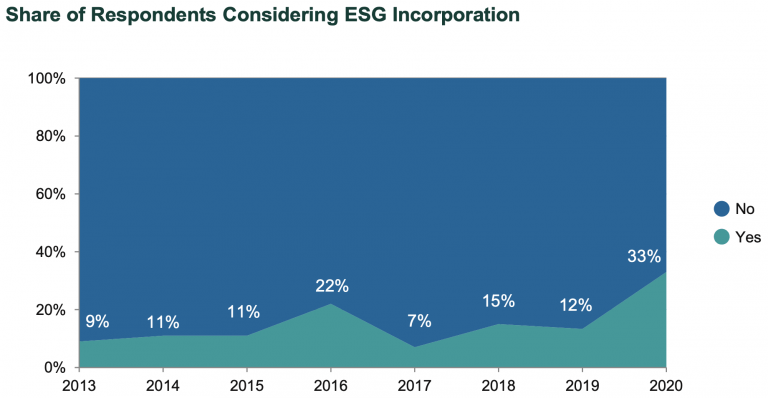
As significantly, we found that 33% of respondents not yet incorporating ESG were considering doing so, the highest in the survey’s history and nearly triple the level in 2019. This brings the ratio of those either incorporating or thinking about incorporating ESG to 61% of the total respondent pool in 2020.
- This year’s ESG Survey, conducted in mid-2020, reflects input from 102 U.S. institutional investors. For this survey, ESG factors include socially responsible investing (SRI, including divestment), sustainable investing, impact investing, and other associated terms. Respondents include public and corporate DB and DC plans, as well as endowments and foundations, ranging in assets under management from small (under $500 million) to large (more than $20 billion). The largest share of respondents (41%) is from the government sector.
Survey highlights:
- Investor type: Public plans (36%) have incorporated ESG factors into the investment decision-making process at a slightly higher rate than their corporate counterparts (32%), but this level of incorporation was still dwarfed by that of endowments (63%) and foundations (57%).
- Investor location: ESG adoption was highest by plans in the Northeast and on the West Coast.
- Those not incorporating it: Despite the trends toward adoption, 56% of respondents did not incorporate ESG into investment decision-making—although as noted earlier, a third of those are considering it.
- Motivations: The most frequently cited reason for incorporating ESG among respondents was to address stakeholder concerns. Conversely, the most frequently cited reason for not incorporating ESG was because the benefits of ESG incorporation were unproven or unclear. When comparing early adopters’ motivations for incorporating ESG versus recent adopters, recent adopters were more likely to be addressing stakeholder concerns and to be focused on an improved risk profile, while early adopters were focused on alignment with their organization’s values and impact.

- Allocations: Only 19% of respondents maintain an ESG allocation separate from their traditional portfolio, indicating broader ESG integration is preferred.
- Implementation: Over half of respondents that incorporate ESG have communicated ESG’s importance to their investment managers, consider ESG with every investment/investment manager selection, and added ESG language to their IPS.
- Coronavirus impact: 60% of respondents said the global COVID-19 pandemic has had no impact on their planned ESG initiatives, while 14% believed the pandemic will cause them to increase their rate of ESG adoption.
- Product interest: Active U.S. equity (33%) led the list of strategies those implementing ESG would like to see more of, followed by active emerging market equity (28%).
- Future direction: 37% of respondents that have incorporated ESG factors in investment decision-making do not plan to make any changes to their usage of ESG factors in the coming years.
This blog post provides a high-level overview of our survey findings. For the entire survey, with detailed data and analysis, please click below.

